Common incidents that can occur in each stage of the wastewater treatment system are: Mechanical, Chemical, and Biological treatment stages. Among them, the microbial tank is where system incidents frequently occur.
Below are some common incidents that occur in each stage of the wastewater treatment system:
1. MECHANICAL TREATMENT STAGE
In wastewater treatment, this stage often encounters the following incidents:
-
Trash jamming in submerged agitators, submerged pumps:
Causes: Due to inadequate coarse trash barriers that fail to block small debris, allowing them to enter subsequent tanks and get caught in the impellers of pumps and agitators, causing jams.
Remedial measures: Additional fine trash barriers can be installed at the collection tank to prevent small debris from entering the system.
-
Unpleasant odor from fine trash barriers:
Causes: Accumulation of excessive waste at the trash barrier, leading to decomposition and the generation of foul odors.
Remedial measures: Regular cleaning and removal of waste from the filter screen.
Read more: Resolving the issue of overloaded wastewater treatment system
2. CHEMICAL TREATMENT STAGE
In wastewater treatment, this stage often encounters the following incidents:
-
The effluent after physical settling has high turbidity and contains a lot of suspended flocs:
Causes: pH is outside the appropriate range (appropriate range is 6.5-8.5), and the contact time between wastewater and chemicals is insufficient.
Remedial measures: This can be addressed by increasing the contact time between chemicals and wastewater within the appropriate timeframe.
-
The effluent after physical settling is yellow:
Causes: Excessive dosing of coagulant chemicals, incomplete reactions in the coagulation tank, resulting in yellow-colored settled wastewater.
Remedial measures: This can be addressed by using an appropriate concentration of chemicals.
3. BIOLOGICAL TREATMENT STAGE
This is the most important and often the most problematic stage in the wastewater treatment system, accounting for about 80% of the overall treatment efficiency. Therefore, it is essential to understand the potential incidents that may occur at this stage in order to devise the most suitable solutions. Some common incidents include:
3.1 Foam Overproduction
Large, increasing foam bubbles covering the surface of the tank. In such cases, it is necessary to check the characteristics of the influent wastewater.

Remedial measures: If the wastewater contains high levels of surfactants (white foam resembling soap bubbles), air sparging and thorough agitation for 30 minutes to 1 hour will gradually reduce and eliminate the foam. If the pH of the wastewater is high (≥8), it is necessary to assess the characteristics of the influent wastewater, adjust the pH to an appropriate level suitable for biological treatment processes, or consider using defoaming agents (though their usage is limited due to high cost).
3.2 Overproduction of foam due to overload
The biomass activity in the treatment tank is insufficiently aerated (below 10% equivalent to MLSS <1000 mg/l). This may occur due to high organic matter concentrations in the biological treatment tank (the COD value in the active biomass tank exceeds the capacity of the aerobic microorganisms by a significant margin. COD>1000 mg/l, shocking the aerobic microorganisms).
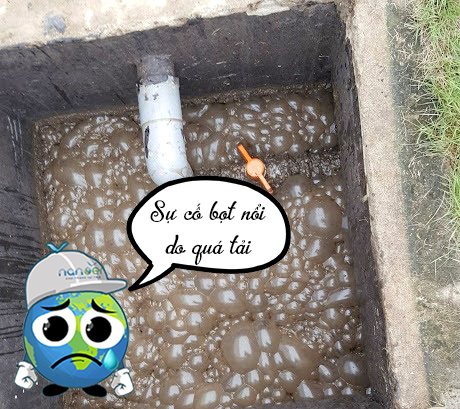

Remedial measures: To address foam overproduction resulting from COD concentrations exceeding the microbial treatment capacity, it is essential to reassess the characteristics of the influent wastewater and the treatment stages preceding the aerobic microbial tank. Additionally, to counter excessive foam caused by a low level of active microorganisms in the tank, supplementing the tank with additional microorganisms is necessary.
3.3 Presence of foam and dark brown sludge on the surface
Dead microorganisms release nutrients, forming gas bubbles on the surface, and dead active biomass sludge adheres to these gas bubbles.
Remedial measures: Immediately rescue the remaining active microorganisms in the aerobic biological tank by turning off aeration for 1 hour and then conducting a wastewater pump-out. Follow this by pumping clean wastewater into the aerated tank for 30 minutes and allowing settling, followed by another wastewater pump-out. Additionally, supplement with additional microorganisms.
3.4 Floating sludge phenomenon in the settling tank
In wastewater containing abundant Nitrosomonas and Nitrobacter microorganisms oxidizing Ammonia to Nitrate, when the microbial sludge passes through the settling tank, it settles at the bottom. As the settled sludge consumes all the dissolved oxygen (DO) in the wastewater stream, the microorganisms become oxygen deficient. This leads to prolonged sludge retention time.
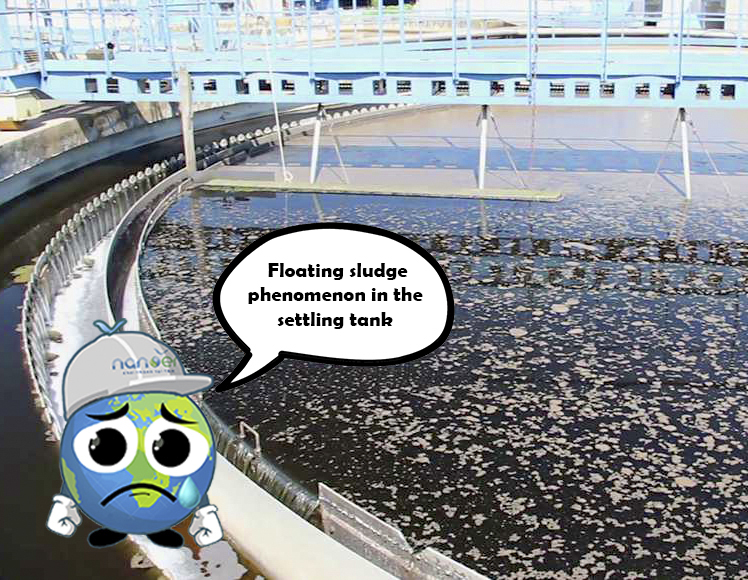

Remedial measure: The temporary solution is to prevent sludge from settling in the settling tank for an extended period by increasing sludge circulation and minimizing dead zones (areas where sludge is not pumped back). Subsequently, the operator should examine the characteristics of the influent wastewater and evaluate the efficiency of Nitrate treatment (denitrification) in the oxygen-deficient biological tank (Anoxic).
3.5 Fine Sludge Issue, Slow Settling, Effluent Turns Yellow after 30 Minutes of Settling
The activated sludge becomes inactive (fine sludge) due to a lack of nutrients (organic matter) for microorganisms. Microorganisms deprived of nutrients fail to thrive, resulting in very fine sludge.
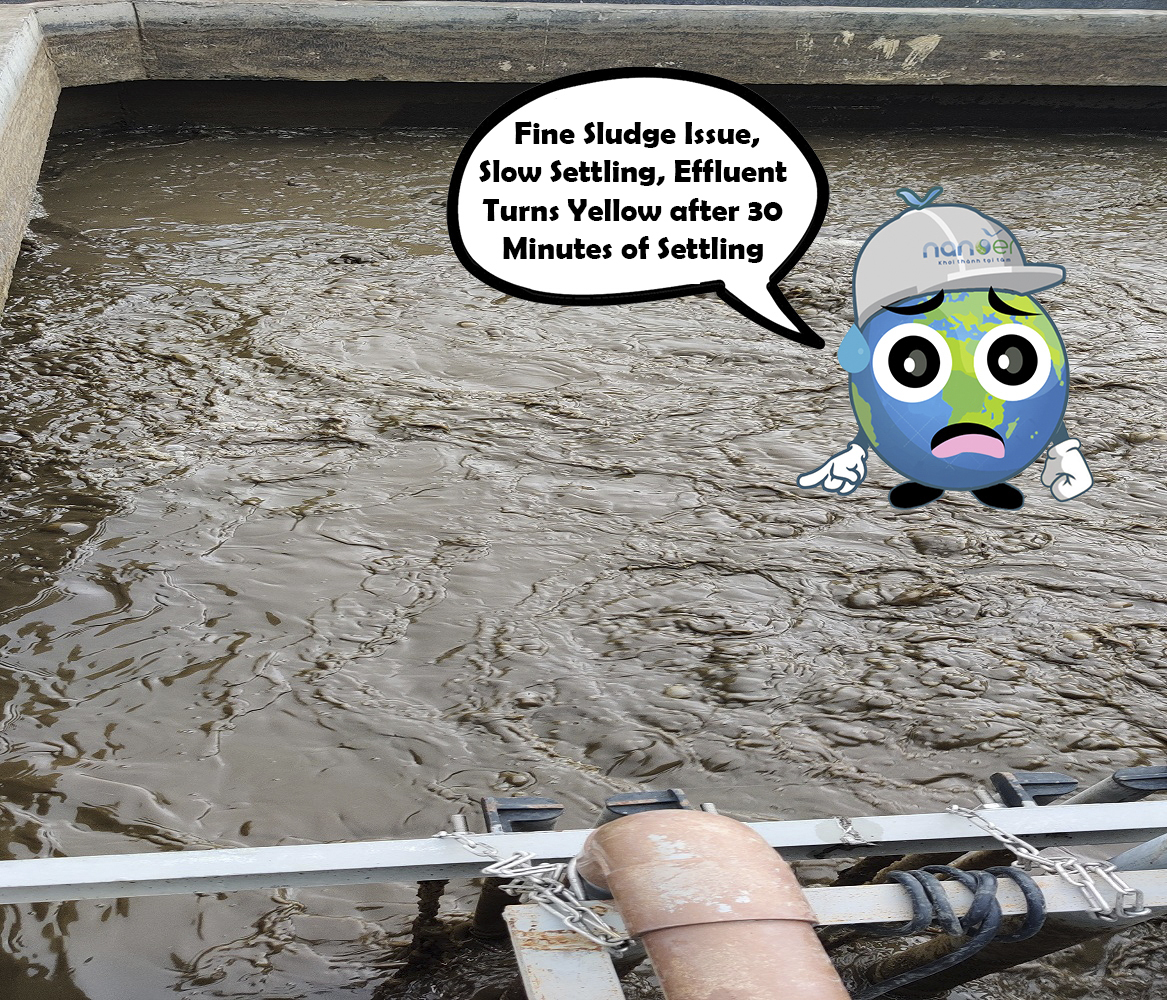

Remedial measure: Increase the nutrient load (food quantity) for microorganisms by: Increasing the flow rate of the wastewater to be treated. Supplementing additional nutrients.
3.6 Brown slimy foam on the surface of the tank
This issue primarily arises due to a low Food to Microorganism Ratio (F/M) and inadequate nutrition, leading to the formation of a layer of slimy foam on the tank's surface. Additionally, the presence of excessive grease in the incoming wastewater acts as an inhibitor to microorganisms, causing them to float on the surface.
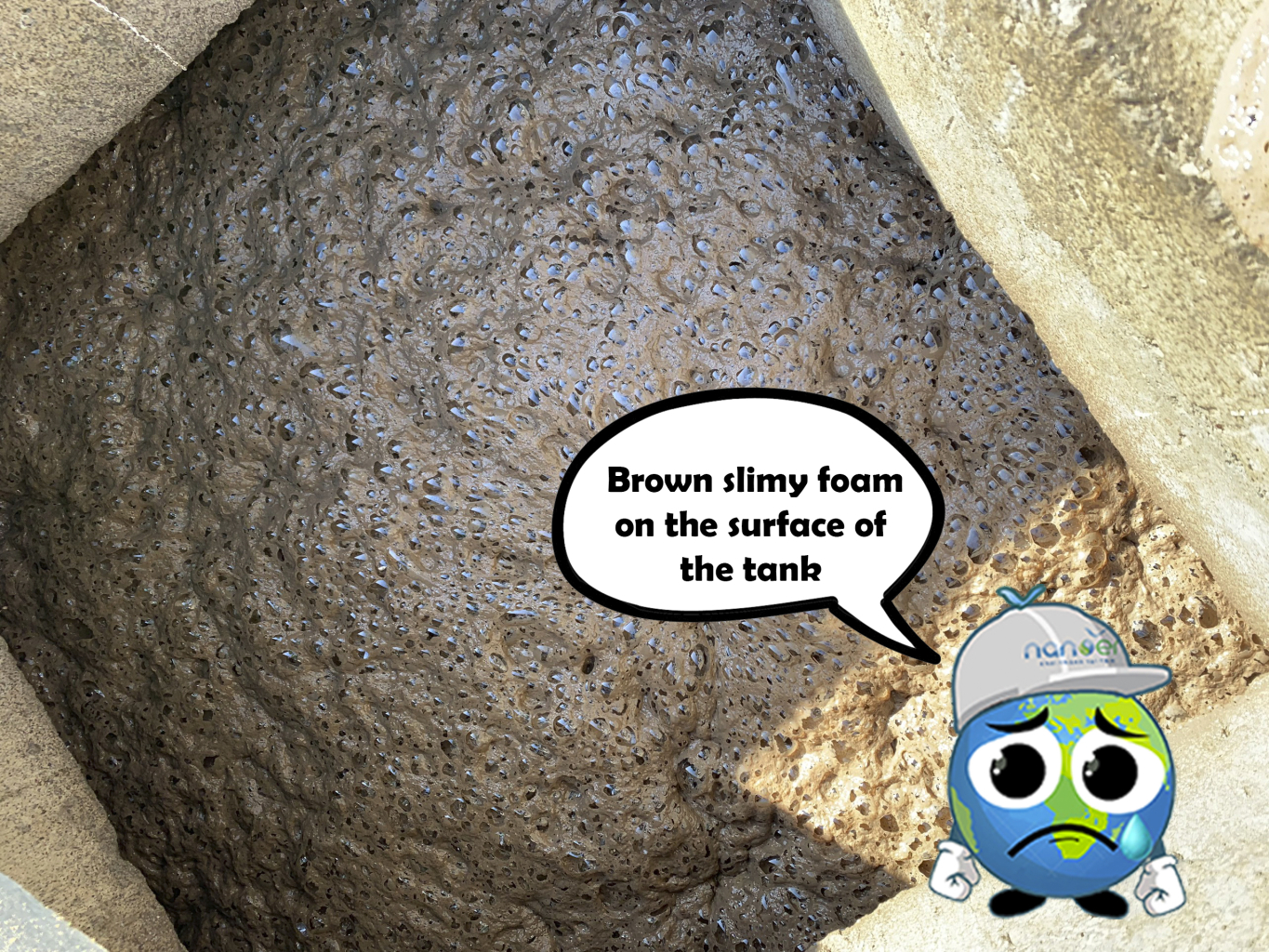

Remedial measure: Reassess the F/M ratio, then proceed to sludge discharge and reduce sludge return by adding more sludge to the tank, increasing the incoming COD, and finally introducing alcohol or ethanol into the tank. It is essential to check and remove grease before introducing wastewater into the biological tank.
During operation, wastewater treatment systems always face potential issues that can arise at any time. This can significantly impact the system's operation and, consequently, negatively affect the production processes of facilities and enterprises. Therefore, operators need to equip themselves with the necessary knowledge to promptly detect and respond to occurring issues within the system, ensuring that businesses can operate smoothly.
Read more: Requirements for wastewater treatment system operators
A reputable provider of environmental dossier services and wastewater treatment system construction
Nanoen is a company operating in the environmental field, and throughout its operation, Nanoen has gained the trust of customers due to its honesty, dedication, and responsibility towards customers and products.
With a team of experienced staff, we offer comprehensive services from environmental dossier consulting to design, construction, operation of environmental treatment systems, reoperation, and supply of microorganisms,...
Nanoen is always ready to provide the best service experience that meets the needs of our customers.
Nanoen
Address: 661E/29, Vo Van Kiet Street, Binh Yen A Quarter, Long Hoa Ward, Binh Thuy District, Can Tho City
Hotline: 0941.777.519 - 0907.803.678 - 0901.229.798
Email: nanoentech@gmail.com
Facebook: www.facebook.com/nanoentech








